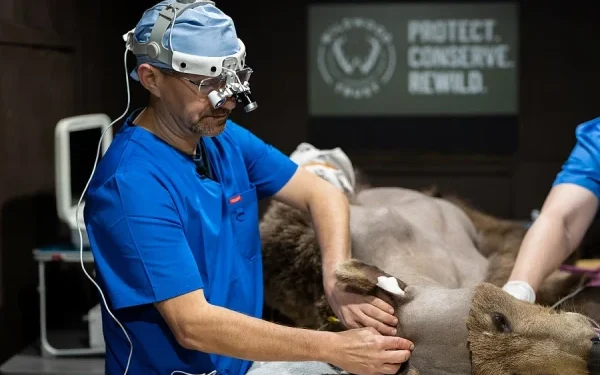
Introduction In an extraordinary medical breakthrough, a brown bear has become the first of its species to undergo brain surgery successfully. The bear, named Bucky, resides at the Wildwood Trust in England, where he received life-saving treatment for a brain abscess. Months after his surgery and subsequent hibernation, Bucky has awakened, displaying positive signs of recovery and improved health.
A Historic Veterinary Achievement Bucky’s surgery marks a groundbreaking moment in veterinary medicine. While brain surgeries are common in humans and even in some domesticated animals, performing such a complex procedure on a large wild animal like a bear was a significant challenge.
The operation, conducted in October, was prompted by concerning symptoms observed in Bucky. He exhibited signs of neurological distress, including difficulty coordinating movements, loss of appetite, and an overall decline in energy levels. After a thorough medical examination, veterinarians diagnosed him with a brain abscess, a potentially fatal condition if left untreated.
The Surgical Procedure and Recovery Process A team of skilled veterinary surgeons, neurologists, and anesthesiologists worked together to carry out the intricate operation. Given the risks associated with brain surgery—especially on a bear—the procedure required careful planning, state-of-the-art imaging technology, and precision in execution.
Following the surgery, Bucky was closely monitored by zoo staff as he entered hibernation for the winter. This period of natural rest allowed his body to heal with minimal stress. However, veterinarians remained cautious, as his true recovery could only be assessed once he emerged from hibernation in the spring.
Signs of a Successful Recovery With the arrival of warmer temperatures, Bucky finally woke up, and to the delight of zoo officials and veterinary staff, he appeared to be in good health. According to a statement released by the Wildwood Trust on social media, Bucky has shown an “extraordinary change” since waking up. He is now active, lively, and behaving just as he did before falling ill.
Zoo officials have not observed any of the pre-surgery symptoms that once plagued Bucky. His successful recovery has been described as a triumph not only for the Wildwood Trust but also for veterinary science as a whole.
What This Means for Veterinary Medicine Bucky’s case sets a precedent for the future treatment of neurological conditions in large wild animals. Historically, many such conditions in wildlife have been considered untreatable due to the complexities involved in surgical intervention. This successful surgery demonstrates that, with advanced technology and medical expertise, even complex procedures like brain surgery can be performed on wild species.
Veterinary professionals hope that this milestone will pave the way for further advancements in animal neurology, potentially benefiting not only bears but also other large mammals suffering from similar conditions.
Public and Scientific Interest in Bucky’s Story Bucky’s journey has captured the interest of wildlife enthusiasts, animal rights activists, and scientists worldwide. Many have praised the Wildwood Trust for their commitment to animal welfare and their willingness to push the boundaries of veterinary medicine.
On social media, supporters have expressed joy and relief at Bucky’s recovery. Wildlife conservationists have also highlighted the importance of providing medical care to animals in captivity, ensuring they receive the best possible quality of life.
Future Monitoring and Care Although Bucky’s initial signs of recovery are promising, Wildwood Trust staff and veterinary experts will continue to monitor him closely in the coming months. Regular health check-ups, neurological assessments, and behavioral observations will be conducted to ensure that he remains in good health.
Experts will also study his case to gather valuable insights into the long-term effects of brain surgery on large mammals. This data could contribute to future research and medical interventions for other animals facing similar health challenges.
Conclusion Bucky’s successful brain surgery and subsequent recovery stand as a remarkable achievement in veterinary medicine and wildlife care. His case provides hope for the future of medical treatment in large wild animals and reinforces the importance of advancing veterinary science. As Bucky continues to thrive, his story serves as a testament to the dedication of those who work tirelessly to protect and care for wildlife.
The world will be watching as Bucky embarks on this new chapter of his life, and his progress will undoubtedly continue to inspire both the veterinary community and animal lovers worldwide.